Repadmin – Active Directory Replication Tools
In this post, we’ll learn about Repadmin command, it’s the Active Directory Replication Tools used to check Active Directory replication between Active Directory Domain Controller. Repadmin is a command line tool introduced by Microsoft in Windows Server 2003 R2 and still actively used in latest version of Microsoft e.g. Windows Server 2012 R2, etc to replicate AD data. In the old post, we already learned the steps to promote a Domain Controller using PowerShell command.
In this post, we’ll learn about Repadmin Command and the steps to check AD Replication between Domain Controllers through GUI and Command Line Tool.
The primary tool to check AD replication is “Repadmin”, it’s a Command line tool that was introduced in Windows Server 2003 r2 and still used extensively to check the replication issues and to forcefully replication AD data.
As we all know and even we have learned in one of the old article that Domain Controllers are used for the centralized management. It is also a centralized repository for all the objects that we have in our domain.
Steps to check AD Replication in Windows Server 2012 R2 through GUI
1. Let’s assume a scenario in which we have two Domain Controllers in our Domain named as DC01 and DC02 in the domain. We’ll check Active Directory objects replication between these two Domain Controller.
2. Active Directory sites and services is a primary console used to replicate the AD objects between the Domain Controllers. We can also manage the objects represent the sites and servers which reside in those sites. Site links are automatically created as and when we add any new Domain Controller in our environment.
To forcefully replicate AD, open Active Directory sites and services console, click on DC02 than right click onNTDS Settings. Under the NTDS Settings “Click on Replicate configuration from the selected DC“. Through this option, we pull the information from the selected DC (FYI, replication is of 2 types i.e. Pull and Push).
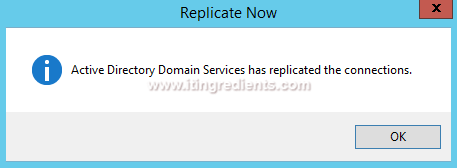
3. It opens the confirmation dialogue box which tells that Active Directory Domain Services are replicated the connections. Click on OK. If you see any error or if Additional Domain Controller is recently promoted then you need to wait for sometime (about 30 minutes if intra-site and about two to four hours if inter-site) before you try to do forceful AD replication.
4. To push the information to selected DC click on “Replicate configuration to the selected DC“. It also opens the confirmation dialogue box that the Active Directory Domain Services are replicated with each other. Click on Next to continue.
It is the preferred method to replicate AD as it’s only going to replicate Data between Domain Controllers that we select. It would not start replication between all the DCs which consumes most of the bandwidth and can create congestion in the environment.
Steps to check AD Replication in Windows Server 2012 R2 through Command Prompt (Repadmin)
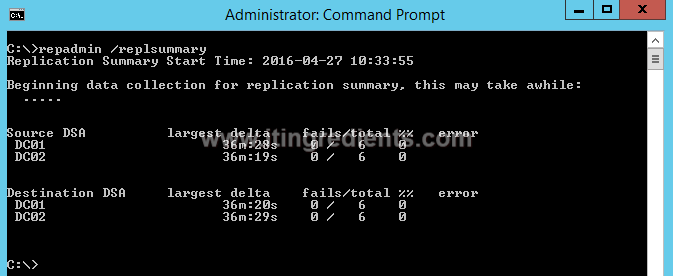
1. The first command that we are run is “Repadmin /replsummary” to check the current replication health between the domain controllers. The “/replsummary” operation quickly and concisely summarizes replication state and relative health of a forest.
After running the command it shows some information which was in two parts – Source DSA and Destination DSA.
What is FSMO Roles (Flexible Single Master Operations)
We can see that both servers are listed in both sections, the reason behind this is the Active Directory uses multi-master domain model. Active Directory can be updated from any writable Domain Controller except the Read-only Domain Controller. The RODC would only be listed in Destination DSA section.
2. The second command is “Repadmin /Queue” shows the elements are remaining in the queue to replicate. It Displays inbound replication requests that the Domain Controller needs to issue to become consistent with its source replication partners.
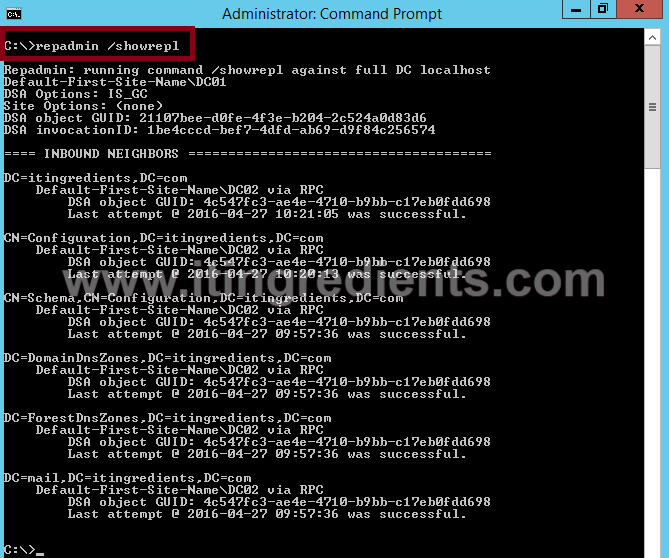
3. The Third command is “Repadmin /Showrepl displays the replication status when the specified domain controller last attempted to implement inbound replication of Active Directory partitions. It helps to figure out the replication topology and replication failure.
4. The Fourth command is “Repadmin /syncall” it Synchronizes a specified domain controller with all replication partners. We recommend you not to run this command in the big environment because it forcefully replicates Active Directory objects between all the domain controller which leads to excessive load on the network and can result in network congestion.
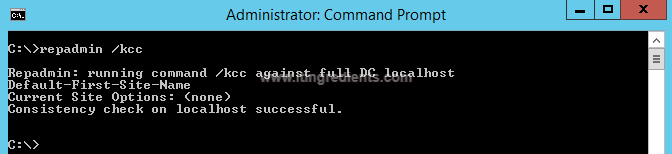
5. Repadmin /KCC this command forces the KCC (Knowledge Consistency Checker) on targeted domain controller(s) to immediately recalculate its inbound replication topology. It checks and creates the connections between the Domain Controllers. By default KCC runs in the background every 15 minutes to check if new connection is established between DCs or not.
By running the command we are forcing DCs to check if new Domain Controller is found in the environment and if yes then add connection to the same.
6. Repadmin /replicate starts the immediate replication of the specified directory partition to the destination domain controller from the source DC.

Conclusion:
Hope you understood all the replication tools that we have mentioned in this article that are used to check AD replication and to Replicate AD using GUI mode and from command prompt. Please feel free to leave your suggestions and comments and questions in the comment section.
Also mention all the scenarios in which you are currently using all the above mentioned command and any issues that you encountered while running them.